数据结构02-压缩链表-ziplist
大约 8 分钟
数据结构02-压缩链表-ziplist
总览
作用于
- 数量比较少的hash、zset
ziplist数据结构
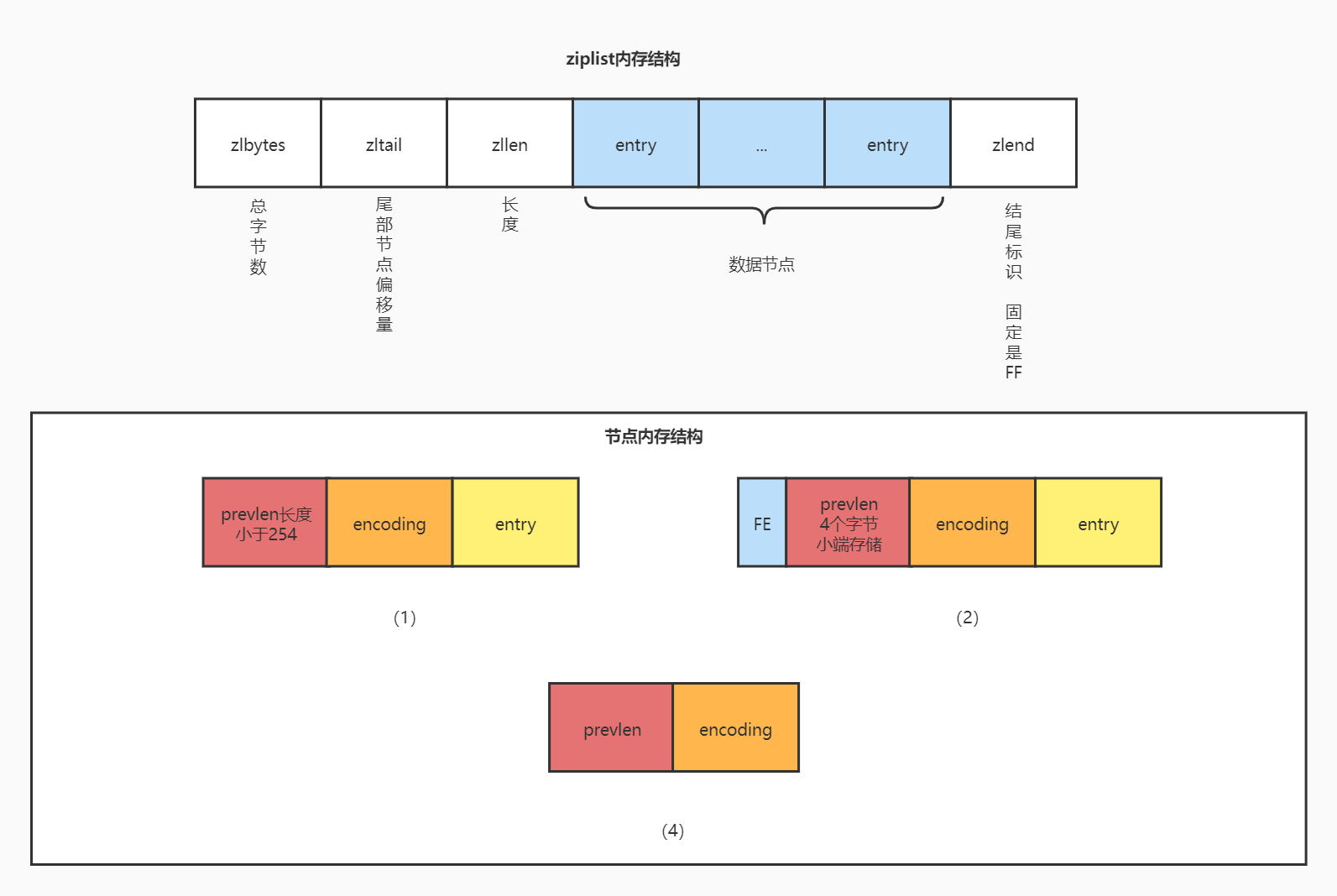
ziplist是一个用一段特殊编码实现的双向链表,优势是占用内存小,可以存储字符串类型和整数类型。在内存布局中包含一下几个字段
- zlbytes:(4 bytes)整个链表占的内存字节数
- zltail:(4 bytes)链表尾部节点的偏移量,存储这个信息的作用是实现反向遍历,因为需要知道尾部的地址才能从尾部向前遍历节点
- zllen:(2 bytes)节点长度
- entry:(n bytes)数据节点,数据节点包含3个结构,下面详细讲解
- zlend:(1 bytes)结束标识符,固定是0xFF
节点数据结构
在6.2的版本中有3种节点数据结构,对不同长度的字符串、数字使用不同的数据结构存储
图(1)
字段
- prevlen:前一个节点的长度
- encoding:编码
- entry:节点数据
满足条件
满足一下条件使用这种数据结构
- 前一个节点的长度小于254bytes
- 如果是数字,满足
x > 12,如果是字符串,满足长度小于254
图(2)
字段
- FE:标识符,固定是
0xFE,作用是识别该数据结构 - prevlen:前一个节点的长度,4个字节小端序列存储
- encoding:编码
- entry:节点数据
满足条件
- 前一个节点的长度大于等于254bytes
图(3)
字段
- prevlen:前一个节点的长度
- encoding:编码
满足条件
- 数字类型,满足
0 <= x >= 12
encoding字段生成逻辑
encoding字段记录了节点数据类型(字符串、数字)和数据长度信息,下面分两种类型进行讲解。
字符串
/* 把encoding写入内存 */
unsigned int zipStoreEntryEncoding(unsigned char *p, unsigned char encoding, unsigned int rawlen) {
/* 默认编码长度是1 */
unsigned char len = 1, buf[5];
/* 判断是否字符串类型, 满足条件 (encoding & 0xc0) < 0xc0 */
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
/* Although encoding is given it may not be set for strings,
* so we determine it here using the raw length. */
/* 字符串长度(包含结束字节`\0`)小于64 */
if (rawlen <= 0x3f) {
if (!p) return len;
/* 编码 = (0 << 6) | rawlen,其实就是长度是什么就存什么*/
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_06B | rawlen;
} else if (rawlen <= 0x3fff) { /* 长度 > 0x3f <= 0x3fff(16,383) */
/* 长度 + 1 = 2*/
len += 1;
if (!p) return len;
/* 下面操作就是rawlen塞到两个字节的内存中 */
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_14B | ((rawlen >> 8) & 0x3f);
buf[1] = rawlen & 0xff;
} else {
/* 长度 + 1 = 5*/
len += 4;
if (!p) return len;
/* 下面操作就是rawlen塞到5个字节的内存中 */
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_32B;
buf[1] = (rawlen >> 24) & 0xff;
buf[2] = (rawlen >> 16) & 0xff;
buf[3] = (rawlen >> 8) & 0xff;
buf[4] = rawlen & 0xff;
}
} else {
/* Implies integer encoding, so length is always 1. */
if (!p) return len;
/* 数字类型的编码由 zipTryEncoding 中生成*/
buf[0] = encoding;
}
/* Store this length at p. */
/* 写入内存 */
memcpy(p,buf,len);
return len;
}
字符串标识如下
#define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0 /* 掩码 */
#define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6) /* 长度<= 63 */
#define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6) /* 长度<= 16,383 */
#define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6) /* 长度> 16,383 */
数字
int zipTryEncoding(unsigned char *entry, unsigned int entrylen, long long *v, unsigned char *encoding) {
long long value;
/* 值的长度大于等于32或者等于0的时候,直接返回 */
if (entrylen >= 32 || entrylen == 0) return 0;
/* 尝试把字符串转成数字类型 long long */
if (string2ll((char*)entry,entrylen,&value)) {
/* Great, the string can be encoded. Check what's the smallest
* of our encoding types that can hold this value. */
/* 数字大于等于0,并且大于等于12时,直接把值存储到编码中 */
if (value >= 0 && value <= 12) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN+value;
} else if (value >= INT8_MIN && value <= INT8_MAX) { /* 8位数字 */
*encoding = ZIP_INT_8B;
} else if (value >= INT16_MIN && value <= INT16_MAX) { /* 16位数字 */
*encoding = ZIP_INT_16B;
} else if (value >= INT24_MIN && value <= INT24_MAX) { /* 24位数字 */
*encoding = ZIP_INT_24B;
} else if (value >= INT32_MIN && value <= INT32_MAX) { /* 32位数字 */
*encoding = ZIP_INT_32B;
} else { /* 64位数字 */
*encoding = ZIP_INT_64B;
}
*v = value;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
其中数字标识值如下
#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4) /* 16位 */
#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4) /* 32位 */
#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4) /* 64位 */
#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4) /* 24位 */
#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe /* 8位 */
如何识别类型
数字的标识都与0xc0或运算,说明数字标识的值都>= 0xc0。而字符串标识的值都小于0xc0
插入数据逻辑
/* Insert item at "p".
* zl:链表指针
* p:节点指针,这个节点的前面插入
* s:数据
* slen:数据长度
* */
unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
/*
* curlen:当前链表字节数
* reqlen:存储*s所需要的字节数
* newlen:链表更新后的字节数
* */
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen, newlen;
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
size_t offset;
int nextdiff = 0;
unsigned char encoding = 0;
long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a value
that is easy to see if for some reason
we use it uninitialized. */
zlentry tail;
/* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */
/* 第一次插入数据的时候,p[0]是ZIP_END */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);
} else {
/* 第一次插入的时候,p[0] == ptail,因为没有数据,首尾的地址是一样的 */
unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);
if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) {
/* 尾插法这个值才不为0 */
prevlen = zipRawEntryLengthSafe(zl, curlen, ptail);
}
}
/* See if the entry can be encoded */
/* 尝试对字符串编码,目前就是把字符串转成数字存储,达到减少内存的作用 */
if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {
/* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */
/* 返回编码后存储所需要的字节 */
reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding);
} else {
/* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipStoreEntryEncoding will use the
* string length to figure out how to encode it. */
reqlen = slen;
}
/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and
* the length of the payload. */
/* 保存前一个节点的长度 */
reqlen += zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,prevlen);
/* 保存编码 */
reqlen += zipStoreEntryEncoding(NULL,encoding,slen);
/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to
* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in
* its prevlen field. */
int forcelarge = 0;
/* 当长度大于等于254的时候,需要申请多4个字节的空间 */
nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0;
if (nextdiff == -4 && reqlen < 4) {
nextdiff = 0;
forcelarge = 1;
}
/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */
/* offset 是链表节点的偏移量 */
offset = p-zl;
/* 新的长度 */
newlen = curlen+reqlen+nextdiff;
/* 重新申请内存 */
zl = ziplistResize(zl,newlen);
/* 链表节点指针 */
p = zl+offset;
/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */
/* 如果链表中已有数据,则需要移动内存 */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
/* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */
/* 移出空间,让新插入的数据留出位置 */
memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff);
/* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */
/* 保存当前节点的长度,写到内存中 */
if (forcelarge)
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+reqlen,reqlen);
else
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+reqlen,reqlen);
/* Update offset for tail */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);
/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take
* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the
* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */
assert(zipEntrySafe(zl, newlen, p+reqlen, &tail, 1));
if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);
}
} else {
/* This element will be the new tail. */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);
}
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
if (nextdiff != 0) {
offset = p-zl;
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);
p = zl+offset;
}
/* Write the entry */
/* 保存前一个节点的长度 */
p += zipStorePrevEntryLength(p,prevlen);
/* 保存当前节点编码 */
p += zipStoreEntryEncoding(p,encoding,slen);
/* 保存数据 */
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
memcpy(p,s,slen);
} else {
zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);
}
/* 更新链表长度 */
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);
return zl;
}
如何定位首尾节点
- zlbytes:(4 bytes)整个链表占的内存字节数
- zltail:(4 bytes)链表尾部节点的偏移量
- zllen:(2 bytes)节点长度
首节点指针:链表指针 - 4 - 4 - 2
尾节点指针:链表指针 - zltail
如何遍历
- 从头到尾遍历:获取首节点的指针,加上当前节点的字节数就是下一个节点的指针了
- 从尾到头遍历:获取尾节点的指针,获取前一个节点的长度。节点指针减去前一个节点的长度就是前一个节点的指针
其他
删除、替换的思路和插入差不多。找到节点的位置,移除/替换这块空间,重新赋值下一个节点的prelen
缺点
压缩链表存在级联更新的问题,当修改某个节点时,需要修改该节点的后面一个节点的prelen,如果prelen的长度也改变了,就会级联更新下去。
总结
可以看出redis在内存方面的优化是下足了功夫。从项目实战的方面,当应用追求高性能的时候,往往都会使用一些rpc框架,因为rpc框架的数据传输不像一般的http + json传输(传输了太多多余的字节,比如http的头部、json的语法标识),在大数据量传输的需求下,可以考虑设计数据压缩协议,减少字节传输。
