数据结构04-快速链表
数据结构04-快速链表
(开局一张图,下面全靠编)
在Redis 3.2之前的版本,Redis使用压缩链表(ziplist)和双端链表(adlist)来实现List。当元素个数比较少的情况下,使用压缩链表,当数据到一定的量,升级为双端链表。这是因为压缩链表可以节省内存空间,但压缩链表的数据是连续的,数据的插入压缩链表需要重新分配内存,这会影响到压缩链表的执行效率,所以升级到双端链表。快速链表是综合考虑时间效率和空间效率引入的新型数据结构。
原理
因为压缩链表的内存是连续的,在插入的时候需要重新分配内存,快速链表的解决方案就是把一整个链表插分成多个压缩链表,通过链表节点的方式串联起来。从而在新的数据插入的时候操作的内存变小了。整体提升时间效率,也能很好的使用压缩链表的空间压缩能力。
数据结构
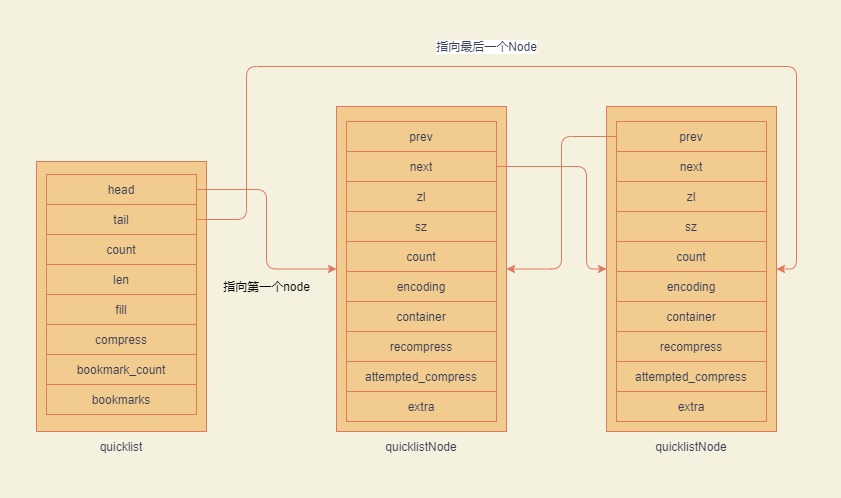
quicklist
/* quicklist is a 40 byte struct (on 64-bit systems) describing a quicklist.
* 'count' is the number of total entries.
* 'len' is the number of quicklist nodes.
* 'compress' is: 0 if compression disabled, otherwise it's the number
* of quicklistNodes to leave uncompressed at ends of quicklist.
* 'fill' is the user-requested (or default) fill factor.
* 'bookmakrs are an optional feature that is used by realloc this struct,
* so that they don't consume memory when not used. */
typedef struct quicklist {
quicklistNode *head;
quicklistNode *tail;
unsigned long count; /* total count of all entries in all ziplists */
unsigned long len; /* number of quicklistNodes */
int fill : QL_FILL_BITS; /* fill factor for individual nodes */
unsigned int compress : QL_COMP_BITS; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */
unsigned int bookmark_count: QL_BM_BITS;
quicklistBookmark bookmarks[];
} quicklist;
- head:头部节点
- tail:尾部节点
- count:链表的元素数量
- len:快速链表中quicklistNode数量
- fill:这个值决定了单个Node的内存空间,后面详细说
- compress:首尾节点不压缩,表示允许压缩节点的数量
quicklistNode
/* quicklistNode is a 32 byte struct describing a ziplist for a quicklist.
* We use bit fields keep the quicklistNode at 32 bytes.
* count: 16 bits, max 65536 (max zl bytes is 65k, so max count actually < 32k).
* encoding: 2 bits, RAW=1, LZF=2.
* container: 2 bits, NONE=1, ZIPLIST=2.
* recompress: 1 bit, bool, true if node is temporary decompressed for usage.
* attempted_compress: 1 bit, boolean, used for verifying during testing.
* extra: 10 bits, free for future use; pads out the remainder of 32 bits */
/*
* 快速链表节点是一个32位大小的结构体,用来描述当前压缩链表的一些属性
* count: 16位,最大值是65536
* encoding:2位,标识是否压缩
* container:2位,这个值在现在的版本只有一个值,2
* recompress:1位,如果是1的话,表示这个压缩链表被压缩过了
* attempted_compress:测试使用
* extra:占位
* */
typedef struct quicklistNode {
struct quicklistNode *prev;
struct quicklistNode *next;
unsigned char *zl;
unsigned int sz; /* ziplist size in bytes */
unsigned int count : 16; /* count of items in ziplist */
unsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */
unsigned int container : 2; /* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */
unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */
unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */
unsigned int extra : 10; /* more bits to steal for future usage */
} quicklistNode;
逻辑
如何判断quicklistNode能否继续插入数据
受quicklist中的fill字段限制
如果fill是负数:fill的值关系到压缩链表的字节大小,关系如下
{-2 , -3 , -4 , -5 , -6 }
{4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536}
计算公式是 (-fill) - 1 = 数组的偏移量,节点的字节数小于对应的值则可以继续插入。
如果fill是正数:fill的值大于8192的话,不允许,如果节点的元素数量小于fill,允许,否则不允许。
初始化
quicklist *quicklistCreate(void) {
struct quicklist *quicklist;
quicklist = zmalloc(sizeof(*quicklist));
quicklist->head = quicklist->tail = NULL;
quicklist->len = 0;
quicklist->count = 0;
/* 是否压缩节点 */
quicklist->compress = 0;
/* -2 意思是一个压缩链表的字节数最大是8k */
quicklist->fill = -2;
quicklist->bookmark_count = 0;
return quicklist;
}
通过quicklistCreate函数初始化,fill的值默认是-2,表示节点中每个压缩链表最大是8K。
数据插入
数据插入分两种情况,一是在链表的首尾插入,二是在链表中的某个节点插入。
首尾插入
原理:先判断首/尾的节点是否还能继续插入数据,如果可以直接插入(调用压缩链表的函数ziplistPush),否则新建一个quicklistNode,替换首/尾节点。
在头部插入代码
int quicklistPushHead(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, size_t sz) {
quicklistNode *orig_head = quicklist->head;
/*
* 判断头节点还能不能插入节点,可以的话在头节点插入
* 否则,新建一个节点
* */
if (likely(
_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(quicklist->head, quicklist->fill, sz))) {
quicklist->head->zl =
ziplistPush(quicklist->head->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(quicklist->head);
} else {
quicklistNode *node = quicklistCreateNode();
node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
_quicklistInsertNodeBefore(quicklist, quicklist->head, node);
}
quicklist->count++;
quicklist->head->count++;
return (orig_head != quicklist->head);
}
在尾部插入代码
int quicklistPushTail(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, size_t sz) {
quicklistNode *orig_tail = quicklist->tail;
if (likely(
_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(quicklist->tail, quicklist->fill, sz))) {
quicklist->tail->zl =
ziplistPush(quicklist->tail->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(quicklist->tail);
} else {
quicklistNode *node = quicklistCreateNode();
node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
_quicklistInsertNodeAfter(quicklist, quicklist->tail, node);
}
quicklist->count++;
quicklist->tail->count++;
return (orig_tail != quicklist->tail);
}
某个值前后插入
我们把在某个元素之前或者之后插入的这个元素称为 基准元素
下面是每个变量的含义
full:基准元素所在的压缩链表是否允许继续插入元素
at_tail:基准元素在压缩链表的尾部
at_head:基准元素在压缩链表的头部
full_next:基准元素所在的链表的下一个链表是否允许插入
full_prev:基准元素所在的链表的上一个链表是否允许插入
after:在基准元素的之前还是之后插入
原理:分为一下几种情况
- 如果没有指定节点,创建一个新的节点,并插入元素,直接返回
- 如果压缩链表没有满,并且是在基准元素之后插入的,直接插入
- 如果压缩链表没有满,并且是在基准元素之前插入的,直接插入
- 基准元素在链表的尾部,要在基准元素之后插入,压缩链表满了,但下一个压缩链表节点没有满,直接在下一个压缩链表插入
- 基准元素在链表的头部,要在基准元素之前插入,压缩链表满了,但上一个压缩链表节点没有满,直接在上一个压缩链表插入
- 基准元素在链表的尾部,要在基准元素之后插入,压缩链表满了,下一个压缩链表节点也满,创建一个新的压缩链表节点,插在中间
- 基准元素在链表的头部,要在基准元素之前插入,压缩链表满了,上一个压缩链表节点也满,创建一个新的压缩链表节点,插在中间
- 基准元素所在的链表满了,但基准元素不在链表的头部和尾部,需要把当前链表节点分裂成两个链表节点,如何插入数据,拼接。
具体的代码如下:
/* 在某个元素的之前或者之后插入 */
REDIS_STATIC void _quicklistInsert(quicklist *quicklist, quicklistEntry *entry,
void *value, const size_t sz, int after) {
/*
* 我们把在某个元素之前或者之后插入的这个元素称为 基准元素
* 下面是每个变量的含义
* full:基准元素所在的压缩链表是否允许继续插入元素
* at_tail:基准元素在压缩链表的尾部
* at_head:基准元素在压缩链表的头部
* full_next:基准元素所在的链表的下一个链表是否允许插入
* full_prev:基准元素所在的链表的上一个链表是否允许插入
* after:在基准元素的之前还是之后插入
* */
int full = 0, at_tail = 0, at_head = 0, full_next = 0, full_prev = 0;
int fill = quicklist->fill;
quicklistNode *node = entry->node;
quicklistNode *new_node = NULL;
/* 如果没有指定节点,创建一个新的节点,并插入元素,直接返回 */
if (!node) {
/* we have no reference node, so let's create only node in the list */
D("No node given!");
new_node = quicklistCreateNode();
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
__quicklistInsertNode(quicklist, NULL, new_node, after);
new_node->count++;
quicklist->count++;
return;
}
/* Populate accounting flags for easier boolean checks later */
if (!_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(node, fill, sz)) {
D("Current node is full with count %d with requested fill %lu",
node->count, fill);
full = 1;
}
if (after && (entry->offset == node->count)) {
D("At Tail of current ziplist");
at_tail = 1;
if (!_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(node->next, fill, sz)) {
D("Next node is full too.");
full_next = 1;
}
}
if (!after && (entry->offset == 0)) {
D("At Head");
at_head = 1;
if (!_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(node->prev, fill, sz)) {
D("Prev node is full too.");
full_prev = 1;
}
}
/* Now determine where and how to insert the new element */
if (!full && after) {
/* 1、压缩链表未满
* 2、在基准元素之后插入
* */
D("Not full, inserting after current position.");
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(node);
unsigned char *next = ziplistNext(node->zl, entry->zi);
if (next == NULL) {
node->zl = ziplistPush(node->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
} else {
node->zl = ziplistInsert(node->zl, next, value, sz);
}
node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, node);
} else if (!full && !after) {
/* 1、压缩链表未满
* 2、在基准元素之前插入
* */
D("Not full, inserting before current position.");
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(node);
node->zl = ziplistInsert(node->zl, entry->zi, value, sz);
node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, node);
} else if (full && at_tail && node->next && !full_next && after) {
/* 1、在基准元素之后插入 */
/* 2、基准元素所在的链表不允许插入,并且基准链表在链表的尾部,但下一个压缩链表还允许插入 */
/* If we are: at tail, next has free space, and inserting after:
* - insert entry at head of next node. */
D("Full and tail, but next isn't full; inserting next node head");
new_node = node->next;
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(new_node);
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(new_node->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, new_node);
} else if (full && at_head && node->prev && !full_prev && !after) {
/* 1、在基准元素的之前插入 */
/* 2、基准元素所在的链表不允许插入,并且基准元素在链表的头部,但上一个压缩链表还允许插入 */
/* If we are: at head, previous has free space, and inserting before:
* - insert entry at tail of previous node. */
D("Full and head, but prev isn't full, inserting prev node tail");
new_node = node->prev;
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(new_node);
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(new_node->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, new_node);
} else if (full && ((at_tail && node->next && full_next && after) ||
(at_head && node->prev && full_prev && !after))) {
/*
* 1、基准元素所在的链表已满
* 2、在基准元素之后插入,基准元素在链表的尾部,但基准元素的下一个链表已满
* 3、在基准元素之前插入,基准元素在链表的头部,但基准元素的上一个链表已满
* */
/* If we are: full, and our prev/next is full, then:
* - create new node and attach to quicklist */
D("\tprovisioning new node...");
new_node = quicklistCreateNode();
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
__quicklistInsertNode(quicklist, node, new_node, after);
} else if (full) {
/* 1、基准元素所在的链表已满 */
/* else, node is full we need to split it. */
/* covers both after and !after cases */
D("\tsplitting node...");
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(node);
new_node = _quicklistSplitNode(node, entry->offset, after);
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(new_node->zl, value, sz,
after ? ZIPLIST_HEAD : ZIPLIST_TAIL);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
__quicklistInsertNode(quicklist, node, new_node, after);
_quicklistMergeNodes(quicklist, node);
}
quicklist->count++;
}
其他
数据的删除、替换、遍历啥的其实和压缩链表都是差不多的,就不具体描述了。
总结
计算机领域有一句名言
“Any problem in computer science can be solved by anther layer of indirection.”
“计算机科学领域的任何问题都可以通过增加一个间接的中间层来解决”
